Horizontal Analysis Meaning, Formula, Examples

Although horizontal analysis primarily focuses on a single company’s performance over time, it can also serve as a basis for comparative analysis when benchmarked against industry peers. Observing how https://www.bookstime.com/ a company’s growth rates in revenue and profit compare with industry averages can offer critical competitive insights. The primary purpose of horizontal analysis is to determine what has happened to financial statement items over time and to identify trends that may affect the health and sustainability of the business. The power of horizontal analysis lies in its ability to transform raw financial data into actionable insights. It helps investors, managers, and analysts discern patterns crucial for forecasting future performance. Whether a company is expanding rapidly, maintaining stability, or facing decline, horizontal analysis offers an indispensable longitudinal perspective for making informed business decisions, budgeting, and strategic planning.
Comparison Period to Base Period Percentage Change Example
- You can also use horizontal analysis in conjunction with both the balance sheet and the income statement.
- To illustrate, consider an investor who wishes to determine Company ABC’s performance over the past year before investing.
- CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
- This can be useful because it allows you to make comparisons across different sets of numbers.
- Horizontal analysis is used to improve and enhance these constraints during financial reporting.
For example, a low inventory turnover would imply that sales are low, the company is not selling its inventory, and there is a surplus. This could also be due to poor horizontal analysis formula marketing or excess inventory due to seasonal demand. Horizontal analysis also makes it easier to detect when a business is underperforming. Insert a column to the right of ‘2022’ and click on the cell corresponding to the first revenue line item.
Financial Accounting II
For example, if a new business strategy was implemented, horizontal analysis helps in measuring the impact of these changes on financial outcomes across subsequent periods. Horizontal analysis provides a dynamic approach to financial statement analysis, offering valuable insights that aid stakeholders in understanding a company’s past trajectories and predicting its future conditions. Based on the horizontal analysis, we observe that Company B’s operating expenses have gradually increased over the three-year period. The growth rates of 10% and 9.09% indicate a consistent upward trend in the company’s expenses. Utilize financial ratios, such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and solvency ratios, to compare the company’s financial performance with industry benchmarks and competitors. This provides a comprehensive view of the company’s relative strengths and weaknesses.
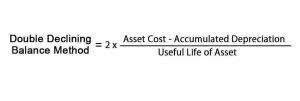
Horizontal Analysis Formula
Since, any line item in a financial statement or financial ratio can be compared across a period of time, it makes the horizontal analysis extremely useful for anyone trying to track a company’s performance over time. Horizontal analysis is often referred to as trend analysis, but the latter term has broader applications and is not specific to financial statements. As the name suggests, trend analysis involves identifying trends and predicting outcomes, which requires analyzing data from multiple consecutive periods. Two popular methods that cover different needs are horizontal and vertical analysis.

Calculate the Percentage Change
- They are also in a position to determine growth patterns and trends, such as seasonality.
- A company’s financial statements – such as the balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement – can reveal operational results and give a clear picture of business performance.
- A horizontal analysis is most useful when the underlying financial information is consistently reported, based on the applicable financial reporting framework.
- Comparability is the ability to review two or more different companies’ financials as a benchmarking exercise.
- In this case, if management compares direct sales between 2007 and 2006 (the base year), it is clear that there is an increase of 3.2%.
The growth rates of 10%, 9.09%, and 8.33% indicate a positive trend in the company’s asset accumulation. Look for consistent positive or negative changes in financial metrics to assess the overall direction and performance of the company. The main difference between horizontal analysis normal balance and vertical analysis is that a horizontal analysis is used to judge performance over a number of reporting periods, while vertical analysis is used to compare numbers within one reporting period.
